在java的数据类型中,包含基本类型 (如:int、double、...) 和包装类型(如: Integer、Double、... )。
自动装箱指的是把基本类型的值转换为对应的包装类对象,反之则为自动拆箱。
如下示例代码:
Integer x = 100;
int y = x;
第一行代码实现了自动装箱,调用了 valueOf(int i) 方法;第二句实现了自动拆箱,调用了 intvalue() 方法。这些都是编译器自动帮我们完成的不用我们自己调用。
以此类推,其他的装箱拆箱机制类似。
下面的代码咋一看,输出都为 true,但其实不然:
Integer a = 100 ;
Integer b = 100 ;
Integer c = 200 ;
Integer d = 200 ;
System.out.println(a==b);
System.out.println(c==d);
其中 a==b 结果为 true , c==d 结果为 false 。出现这种情况,主要是在进行自动装箱时, Integer的缓存机制导致的。
如下Integer部分源码:
public final class Integer extends Number implements Comparable<Integer> {
@Native
public static final int MIN_VALUE = 0x80000000;
@Native
public static final int MAX_VALUE = 0x7fffffff;
// ...
//缓存类 默认用数组缓存 [-128,127] 的常量
private static class IntegerCache {
static final int low = -128;
static final int high;
static final Integer cache[];
static {
// high value may be configured by property
int h = 127;
//获取Jvm配置的Integer的最大值,可以手动设置
String integerCacheHighPropValue =
sun.misc.VM.getSavedProperty("java.lang.Integer.IntegerCache.high");
if (integerCacheHighPropValue != null) {
try {
//转换成int
int i = parseInt(integerCacheHighPropValue);
i = Math.max(i, 127);
// Maximum array size is Integer.MAX_VALUE
h = Math.min(i, Integer.MAX_VALUE - (-low) - 1);
} catch (NumberFormatException nfe) {
// If the property cannot be parsed into an int, ignore it.
}
}
high = h;
//创建缓存常量数组
cache = new Integer[(high - low) + 1];
int j = low;
//设置数组元素值
for (int k = 0; k < cache.length; k++)
cache[k] = new Integer(j++);
//通过断言确保数组最小范围为:[-128,127]
assert IntegerCache.high >= 127;
}
private IntegerCache() {
}
}
//...
/**
* 自动装箱
*
* int -> Integer
*
* @param i
* @return
*/
public static Integer valueOf(int i) {
//如果在缓存范围内,直接从缓存中区,
if (i >= Integer.IntegerCache.low && i <= Integer.IntegerCache.high)
return Integer.IntegerCache.cache[i + (-Integer.IntegerCache.low)];
// 在缓存空间外,重新创建
return new Integer(i);
}
//...
}
在默认情况下,Integer创建的缓存常量为 [-128,127],所以在上面的例子中,Integer a = 100 创建 a 对象是直接从常量数组中获取的,直接找到他的引用,b也是同样的,则 a==b 返回true;对于 Integer c = 200 ,在常量池中没有缓存 ,则 通过 new Integer(200) 创建新对象,d也是这样创建的,他们所指向的引用不同,则 c==d 返回为 false 。
在上面的 缓存类 IntegerCache 中的静态代码块中,使用 sun.misc.VM.getSavedProperty("java.lang.Integer.IntegerCache.high");
获取设置jvm最大的Integer缓存池范围。可以手动指定该值,通过设置 -XX:AutoBoxCacheMax=2000 属性,如下命令行编译:
//编译生成字节码
javac TestInteger.java
//指定范围最最大值为2000,运行
java -XX:AutoBoxCacheMax=2000 TestInteger
此时如下代码输出均为true:
Integer a = 100 ;
Integer b = 100 ;
Integer c = 200 ;
Integer d = 200 ;
System.out.println(a==b);
System.out.println(c==d);
如果使用ide,直接设置 运行时 VM 值即可,如下图
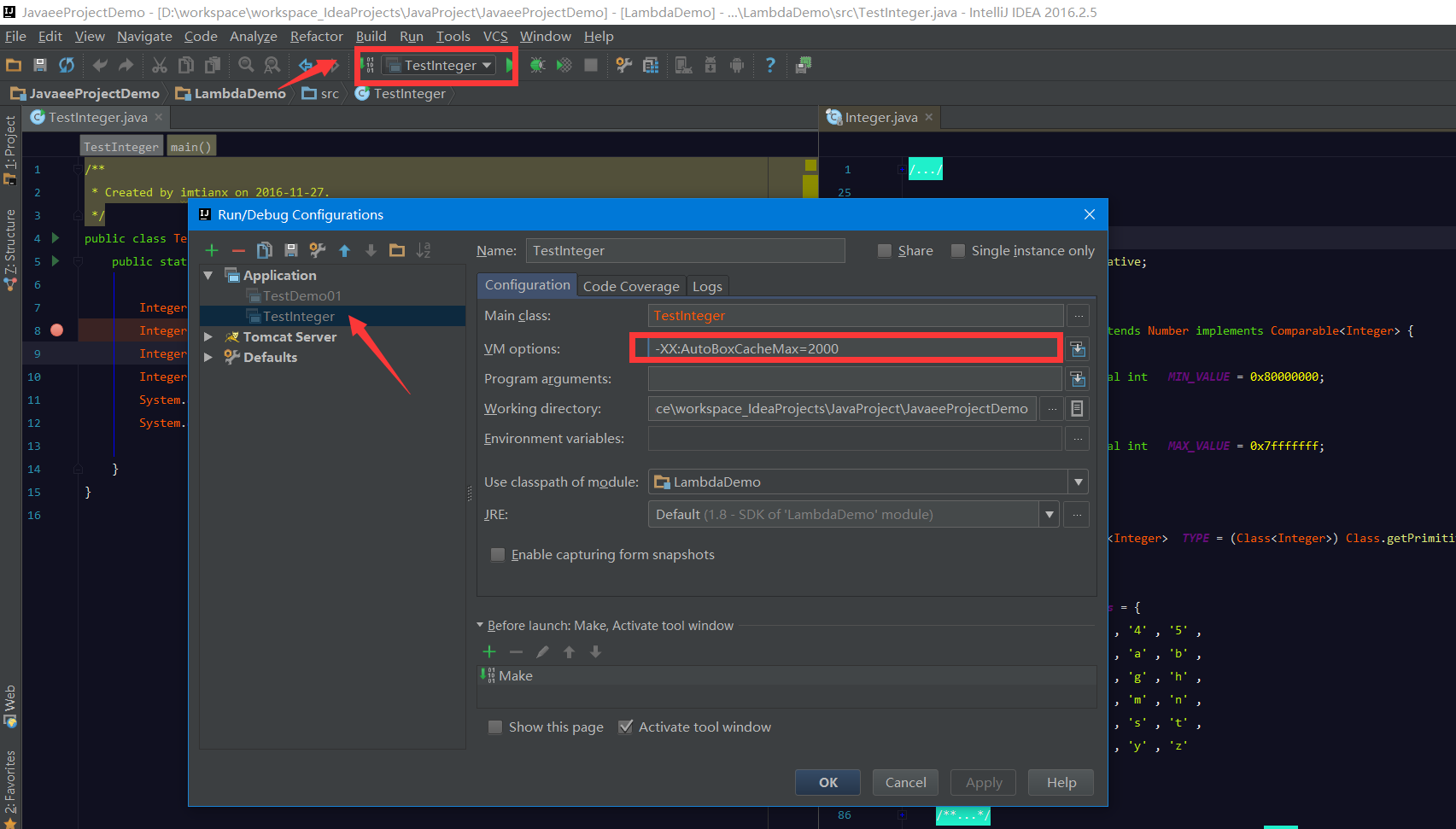
此外,在上面的代码中用到了 assert(断言) 关键字,它主要用来保证代码的正确性。
使用发方法为
assert 表达式;
若表达式为 true ,则程序正常运行,否则 抛出异常 java.lang.AssertionError。编辑器默认的是将他关闭的,此时就算表达式为false也没有任何效果。
在idea中开启断言的方式和上面设置 vm值一样,只是这里设置的 是 -ea 。
可使用下面代码测试:
boolean isOpen = false;
assert isOpen;
System.out.println(isOpen);
开启前打印为false,开启后打印为true 。




